Maintaining a Legionella log book safeguards health and ensures legal compliance by documenting critical water system checks. Accurate records of temperature readings, inspections, and maintenance help prevent bacterial growth and demonstrate due diligence. This guide offers practical advice to keep your log book thorough and up to date, protecting both occupants and your organisation from potential risks.
Essential Requirements and Search Intent for Legionella Log Books
Within the water safety sector, the Legionella Log Book plays a vital role in meeting both regulatory and health requirements. This page explains it in detail: Legionella Log Book. UK Health and Safety Executive guidance (notably ACOP L8) mandates that every premises with water systems at risk for legionella—such as care homes, educational sites, rental properties, and commercial buildings—must establish a robust log book. The log is central for documenting regular risk assessments, describing the written scheme of control, tracking remedial actions, and recording outcomes of inspections and water temperature checks. Failure to maintain these records may result in legal non-compliance or increased risk during an HSE audit.
Also to see : Professional Mental Health Services in Dubai: Well-being Assured
For compliance, a standard log book should include: a clear management responsibility structure, site-specific risk assessments, up-to-date schematic diagrams, routine monitoring (including weekly, monthly, and annual checks), a temperature log, flushing records for infrequently used outlets, COSHH information, audit results, and training records. Many facilities rely on downloadable, printable templates or opt for electronic log books to simplify accessibility and updates.
Accurate record keeping—whether on paper or digital—supports best practices, improves response to outbreaks, and provides traceability during audits. Choosing between formats often rests on site complexity, team size, and user preference for updating logs in real time.
Topic to read : Transforming dementia care in rural areas: cutting-edge telehealth solutions for uk geriatricians
Structure and Contents of an Effective Legionella Log Book
Precision: An effective Legionella log book must document management responsibilities, include schematic system drawings, hold up-to-date risk assessments, maintain a written scheme of control, and store COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) information. It should also track comprehensive maintenance and service records, such as water temperature checks, system flushing, microbial sampling, inspection visits, and detailed staff training logs.
Breakdown of Sections:
- Management responsibilities: Clearly define who oversees legionella control tasks and ensure their details are up to date.
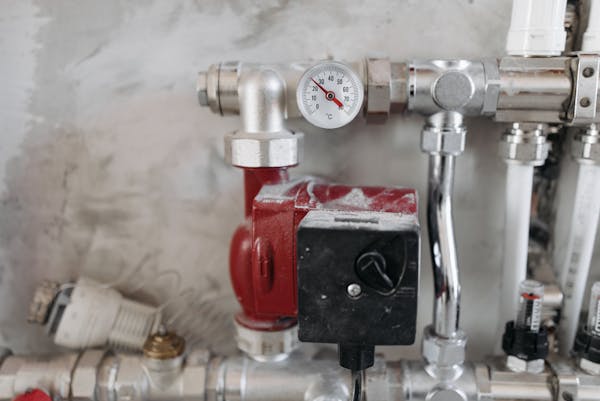
- Schematic system diagrams: Provide a visual layout of your water systems to aid in risk identification.
- Risk assessments & written scheme of control: Show when and how risk has been evaluated, and list control measures for every area at risk.
- COSHH & health and safety information: Log all chemicals or descalers used and their safe handling and storage.
- Maintenance, flushing, and temperature records: Record water temperatures regularly using a legionella water temperature checks template. Maintain legionella flushing record sheets to demonstrate that little-used outlets are regularly flushed as required.
- Microbial sampling sheets & training logs: Document sampling results and training records to show ongoing staff competence.
Accessibility: Store your log book in a central, secure location. It must always be easily accessible for inspection during audits, outbreaks, or routine checks. This ensures compliance and swift response to any issues detected.
Best Practices for Maintenance, Recording, and Monitoring
Precision: Maintain comprehensive records of all Legionella-related monitoring, following a set routine. Use standardized templates or log books to capture temperature readings, flushing events, inspections, and servicing activities. Record water temperatures at key outlets and note corrective actions where values fall outside safe ranges. Ensure flushing of little-used taps occurs and is logged at the recommended frequency. Entries must be timely, accurate, and legible, with responsibility assigned and records retained per legal guidance.
Maintaining accurate water temperature records is central to controlling Legionella. Regular temperature checks at sentinel outlets—such as tanks, calorifiers, and representative taps—help verify that hot water stays above 50°C and cold water below 20°C, denying Legionella its optimum growth range (20-45°C).
Adopting a consistent legionella monitoring schedule is key. Typically, temperature checks are performed every month, while flushing of little-used water outlets occurs weekly. Use templates or dedicated log sheets for uniform entries—errors can lead to compliance failures.
Thorough records not only inform ongoing risk management but are also a statutory requirement under HSE ACOP L8. Missing entries, untimely updates, or incomplete logs are all common pitfalls that can undermine a control plan and affect audit outcomes.
A well-maintained log book supports audit-readiness and demonstrates accountability for those responsible for water hygiene, providing a reliable reference for inspections or in the event of an outbreak.
Tools, Templates, and Compliance Resources for Legionella Management
Precision: A compliant legionella log book records all control tasks—risk assessments, routine water temperature checks, flushing, cleaning, and sampling—as required by HSE’s ACOP L8. These records, whether digital or paper, must be structured, accurate, and readily available for inspection. Documentation should cover the management structure, system schematics, cleaning schedules, maintenance logs, COSHH data, and evidence of staff training.
A wide variety of log book templates, including PDF and printable options, exist for landlords and facility managers. Free downloadable forms help users document water temperatures, flushing activities, and monitoring regimes efficiently. Templates often highlight temperature checks—recording whether outlets reach above 50°C for hot or stay below 20°C for cold, as this is critical for legionella control. Pre-filled and blank formats cater to both landlords managing compliance and businesses with extensive water systems.
Switching to electronic log books is increasingly popular. These allow for automated scheduling, digital signatures, safe cloud storage, and instant audit readiness, reducing paper clutter and minimizing lost records. Integrating log book updates with regular risk assessments lets responsible staff rapidly address flagged issues, ensuring ongoing compliance with UK statutory requirements. Regular training resources, such as online courses or on-site workshops, support staff in maintaining robust, accurate records.